LEMP is a combination of free, open source software. The acronym LEMP refers to the first letters of Linux (Operating system), Nginx Server, MySQL (database software), and PHP, PERL or Python, principal components to build a viable general purpose web server.
Install Nginx Web Server
First, we will start by installing the Nginx web server. To complete the installation, use the following command:
yum install nginx -yOutput:
[root@server ~]# yum install nginx -y
AlmaLinux 9.0-beta - BaseOS 5.9 kB/s | 3.9 kB 00:00
AlmaLinux 9.0-beta - AppStream 6.9 kB/s | 3.9 kB 00:00
AlmaLinux 9.0-beta - Extras packages 7.3 kB/s | 3.8 kB 00:00
Dependencies resolved.
================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Installing:
nginx x86_64 1:1.20.1-9.el9.alma appstream 594 k
Installing dependencies:
almalinux-logos-httpd noarch 90.4-1.el9 appstream 14 k
nginx-filesystem noarch 1:1.20.1-9.el9.alma appstream 11 k
Transaction Summary
================================================================================
Install 3 PackagesOnce the installation is complete, enable Nginx (to start automatically upon system boot), start the web server and verify the status using the commands below.
systemctl start nginx
systemctl enable nginx
systemctl status nginxOutput:
[root@server ~]# systemctl status nginx
● nginx.service - The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2022-05-21 14:19:22 CEST; 15s ago
Main PID: 1122 (nginx)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 5912)
Memory: 1.9M
CPU: 29ms
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
├─1122 "nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx"
└─1123 "nginx: worker process"Check Nginx version
nginx -vOutput:
[root@server ~]# nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.20.1To make your pages available to public, you will have to edit your firewall rules to allow HTTP requests on your web server by using the following commands.
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
firewall-cmd --reloadOutput:
[root@server ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
success
[root@server ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
success
[root@server ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
successVerify that the web server is running and accessible by accessing your server’s IP address.
From your browser,
http://IP_address We need to make user nginx as the owner of web directory. By default it’s owned by the root user.
We need to make user nginx as the owner of web directory. By default it’s owned by the root user.
chown nginx:nginx /usr/share/nginx/html -RInstall MariaDB Server
MariaDB is a popular database server. The installation is simple and requires just a few steps as shown.
yum install mariadb-server mariadb -yOutput:
[root@server ~]# yum install mariadb-server mariadb -y
Last metadata expiration check: 0:16:43 ago on Sat May 21 14:17:41 2022.
Dependencies resolved.
=========================================================================================================================
Package Architecture Version Repository Size
=========================================================================================================================
Installing:
mariadb x86_64 3:10.5.13-1.el9 appstream 1.6 M
mariadb-server x86_64 3:10.5.13-1.el9 appstream 9.3 M
Installing dependencies:
checkpolicy x86_64 3.3-1.el9 appstream 339 k
libaio x86_64 0.3.111-13.el9 baseos 23 k
mariadb-common x86_64 3:10.5.13-1.el9 appstream 27 k
mariadb-connector-c x86_64 3.2.6-1.el9_0 appstream 194 k
mariadb-connector-c-config noarch 3.2.6-1.el9_0 appstream 9.7 k
mariadb-errmsg x86_64 3:10.5.13-1.el9 appstream 183 k
mysql-selinux noarch 1.0.4-2.el9 appstream 35 k
perl-AutoLoader noarch 5.74-479.el9 appstream 30 k
perl-B x86_64 1.80-479.el9 appstream 188 k
perl-Carp noarch 1.50-460.el9 appstream 29 k
perl-Class-Struct noarch 0.66-479.el9 appstream 31 k
perl-DBD-MariaDB x86_64 1.21-15.el9 appstream 151 k
perl-DBI x86_64 1.643-9.el9 appstream 700 k
perl-Data-Dumper x86_64 2.174-462.el9 appstream 55 k
perl-Digest noarch 1.19-4.el9 appstream 25 kOnce the installation is complete, enable MariaDB (to start automatically upon system boot), start the MariaDB and verify the status using the commands below.
systemctl start mariadb
systemctl enable mariadb
systemctl status mariadbOutput:
[root@server ~]# systemctl status mariadb
● mariadb.service - MariaDB 10.5 database server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2022-05-21 14:35:32 CEST; 40s ago
Docs: man:mariadbd(8)
https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/systemd/
Main PID: 3748 (mariadbd)
Status: "Taking your SQL requests now..."
Tasks: 11 (limit: 5912)
Memory: 77.3M
CPU: 594ms
CGroup: /system.slice/mariadb.service
└─3748 /usr/libexec/mariadbd --basedir=/usrFinally, you will want to secure your MariaDB installation by issuing the following command.
mysql_secure_installationOutput:
[root@server ~]# mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success! Once secured, you can connect to MySQL and review the existing databases on your database server by using the following command.
mysql -e "SHOW DATABASES;" -pOutput:
[root@server ~]# mysql -e "SHOW DATABASES;" -p
Enter password:
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
+--------------------+
[root@server ~]#Install PHP
To Install PHP-FPM by running the following command.
yum install php php-mysqlnd php-fpm php-opcache php-gd php-xml php-mbstring -yOutput:
[root@server ~]# yum install php php-mysqlnd php-fpm php-opcache php-gd php-xml php-mbstring -y
Last metadata expiration check: 0:24:55 ago on Sat May 21 14:17:41 2022.
Dependencies resolved.
=========================================================================================================================
Package Architecture Version Repository Size
=========================================================================================================================
Installing:
php x86_64 8.0.13-1.el9 appstream 13 k
php-fpm x86_64 8.0.13-1.el9 appstream 1.6 M
php-gd x86_64 8.0.13-1.el9 appstream 45 k
php-mbstring x86_64 8.0.13-1.el9 appstream 475 k
php-mysqlnd x86_64 8.0.13-1.el9 appstream 154 k
php-opcache x86_64 8.0.13-1.el9 appstream 511 k
php-xml x86_64 8.0.13-1.el9 appstream 136 k
Installing dependencies:
apr x86_64 1.7.0-11.el9 appstream 123 k
apr-util x86_64 1.6.1-20.el9 appstream 95 k
apr-util-bdb x86_64 1.6.1-20.el9 appstream 13 k
dejavu-sans-fonts noarch 2.37-18.el9 baseos 1.3 M
fontconfig x86_64 2.13.94-2.el9 appstream 272 k
fonts-filesystem noarch 1:2.0.5-7.el9.1 baseos 9.0 k
freetype x86_64 2.10.4-6.el9 baseos 387 kOnce the installation is complete, enable php-fpm (to start automatically upon system boot), start the php-fpm and verify the status using the commands below.
systemctl start php-fpm
systemctl enable php-fpm
systemctl status php-fpmOutput:
[root@server ~]# systemctl status php-fpm
● php-fpm.service - The PHP FastCGI Process Manager
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2022-05-21 14:46:44 CEST; 13s ago
Main PID: 4722 (php-fpm)
Status: "Processes active: 0, idle: 5, Requests: 0, slow: 0, Traffic: 0req/sec"
Tasks: 6 (limit: 5912)
Memory: 12.5M
CPU: 87ms
CGroup: /system.slice/php-fpm.service
├─4722 "php-fpm: master process (/etc/php-fpm.conf)"
├─4723 "php-fpm: pool www"
├─4724 "php-fpm: pool www"
├─4725 "php-fpm: pool www"
├─4726 "php-fpm: pool www"
└─4727 "php-fpm: pool www"By default, PHP-FPM runs as the apache user. Since we are using Nginx web server, we need to change following line.
vi /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
user = apache
group = apacheChange them to
user = nginx
group = nginxOnce changed, need to reload php-fpm
systemctl reload php-fpmTest your PHP, by creating a simple info.php file with a phinfo() in it. The file should be placed in the directory root for your web server, which is /usr/share/nginx/html/info.php.
To create the file use:
echo "<?php phpinfo() ?>" > /usr/share/nginx/html/info.phpRestart the Nginx and PHP-FPM.
systemctl restart nginx php-fpmNow again, access http://localhost/info.php or http://yourserver-ip-address/info.php. You should see a page similar to below one.
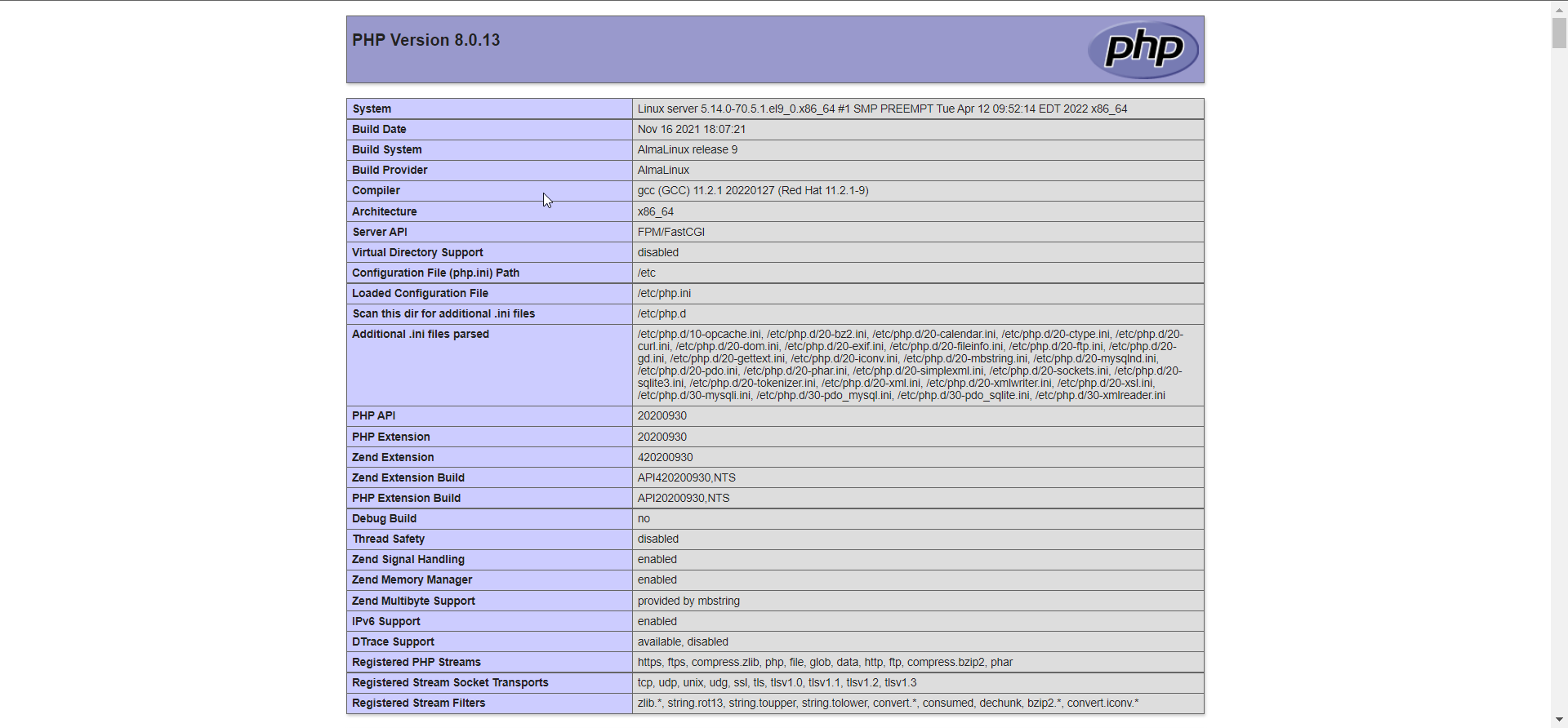
Done!
